Jobs to be done
Jobs to be Done (JTBD) is a tool that helps with understanding why customers buy things. Instead of just looking at the product, the focus is on what people are trying to achieve when they use it. The key question is “What job is the customer trying to get done with this product?” This means focusing on what people need and how they feel when they choose what to buy.
Key concepts important in generating JTBD:
Customer Segments: Different customer groups that an organisation targets with products or services
Functional Dimensions: How well something works and meets practical needs.
Example: A phone’s functional aspect is its ability to make calls
Emotional Dimensions: The feelings and emotions something evokes in you.
Example:A phone’s emotional aspect may be providing users with a sense of safety through features such as emergency contact access and location sharing
Personal Dimensions: How something aligns with your personal identity or preferences.
Example: A phone often serves as a tool that fits seamlessly into a user’s lifestyle. This includes apps and features that cater to specific interests or daily routines
Social Dimensions: How something influences or reflects your interactions and relationships with others.
Example: Choosing an iphone over other types of phones can be a result of social pressure to keep up with peers.
The results
- A deep understanding of customer needs and motivations
- Targeted product or service improvements aligned to customer ‘jobs’
- Clarity on how the product or service can stand-out from the competition
- Insights to inform marketing, product development and sales approaches
When to use it
Product development: When creating new products or services
Market segmentation: When categorising groups of customers based on what they want to achieve
Innovation: When looking to uncover new opportunities
Improving customer experience: When trying to make improvements to products or services for customers
Strengths
Customer-centric
Helps uncover emerging trends
Versatile across industries
Supports innovation
Weaknesses
Can be time consuming
Insights can be limited depending on scope
Can be difficult to get deep insights
How to use it?
What do I need to start?
Examples of inputs:
- Clarity on target customer segments. You can use customer segmentation analysis to do this
- Target customer insights, such as insights from surveys on their needs and preferences
- Insights from observing customers interacting with products or services in real-life situations.
- Market research and competitive analysis
How to use it?
Who to involve?
- A small team willing to go deeper with customers
- Representatives who can provide customer insights
- People with knowledge of competitors
- People who can take the findings from JTBD and market the product or service
Step by step
1
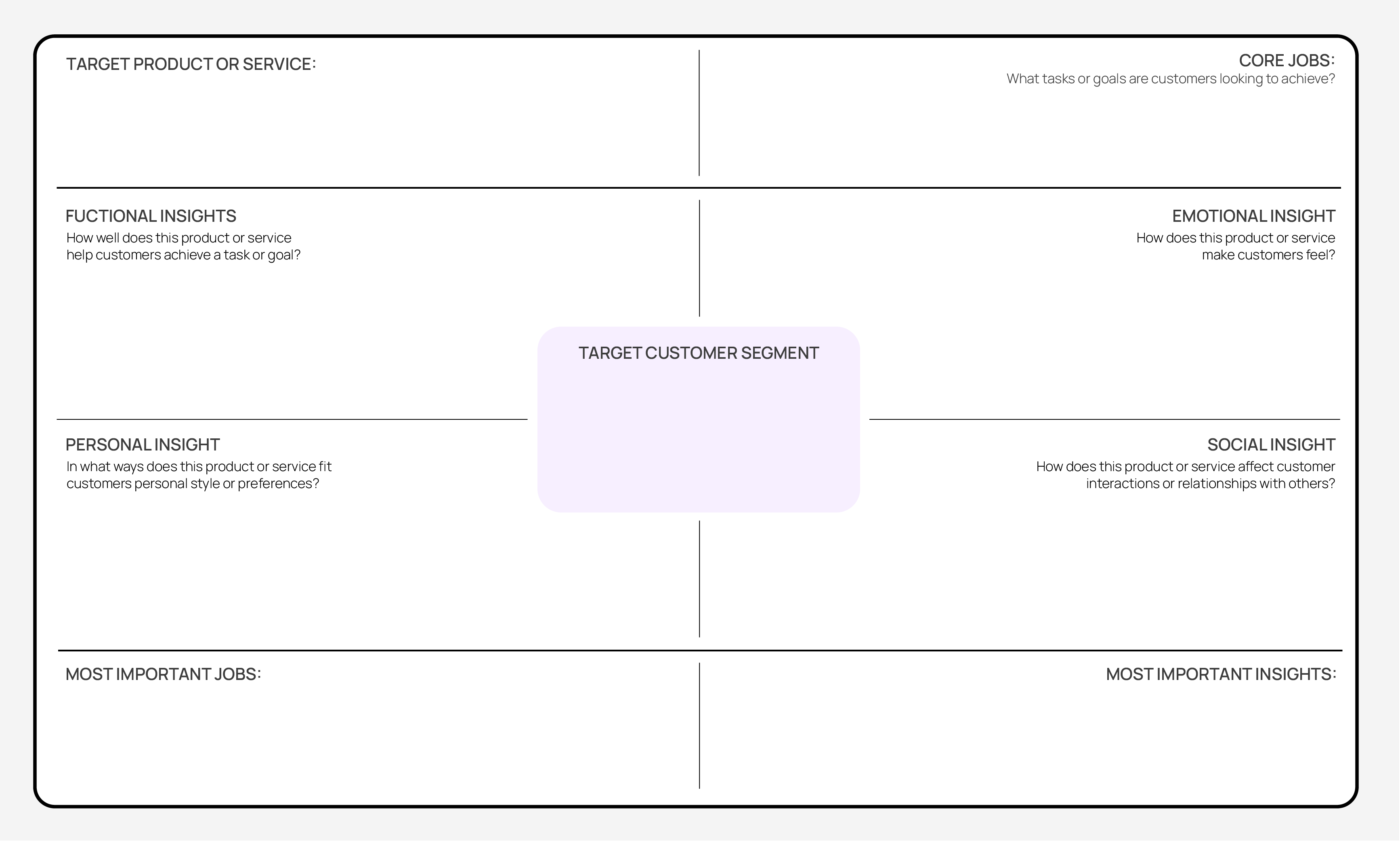
Define the customer segments
Identify and agree on the most important customer segments.
Compile and review any insights available on the target customer segments.
Use one canvas for each customer segment.
2
Define the core ‘jobs’
For each customer segment, identify the customer jobs. Ask questions like:
- What tasks or goals are customers looking to achieve?
- What problems are customers trying to solve?
3
Identify and categorise job insights
For each customer segment, identify and categorise different insights relating to the job to be done
Questions to surface this include:
- Functional: How well does this product or service help customers achieve a task or goal?
- Emotional: How does this product or service make customers feel?
- Personal: In what ways does this product or service fit customers personal style or preferences?
- Social: How does this product or service affect customer interactions or relationships with others?
4
Prioritise
Decide which jobs are most important. Ask questions like:
- Which jobs do customers have the strongest need for?
- What jobs are customers trying to do most often?
Identify which job dimensions are the strongest drivers for customers.
5
Design solutions
Design or refine products or services that address the prioritised jobs
Consider using these design tools to support solution design:
-
- Double Diamond
- Service blueprint
- MVP
- Process mapping
6
Validate and refine
Test solutions with customers to see whether the product or service meets the needs of the job. Use customer feedback to refine.