SWOT
SWOT is an analysis tool often used in strategic planning processes. SWOT stands for:
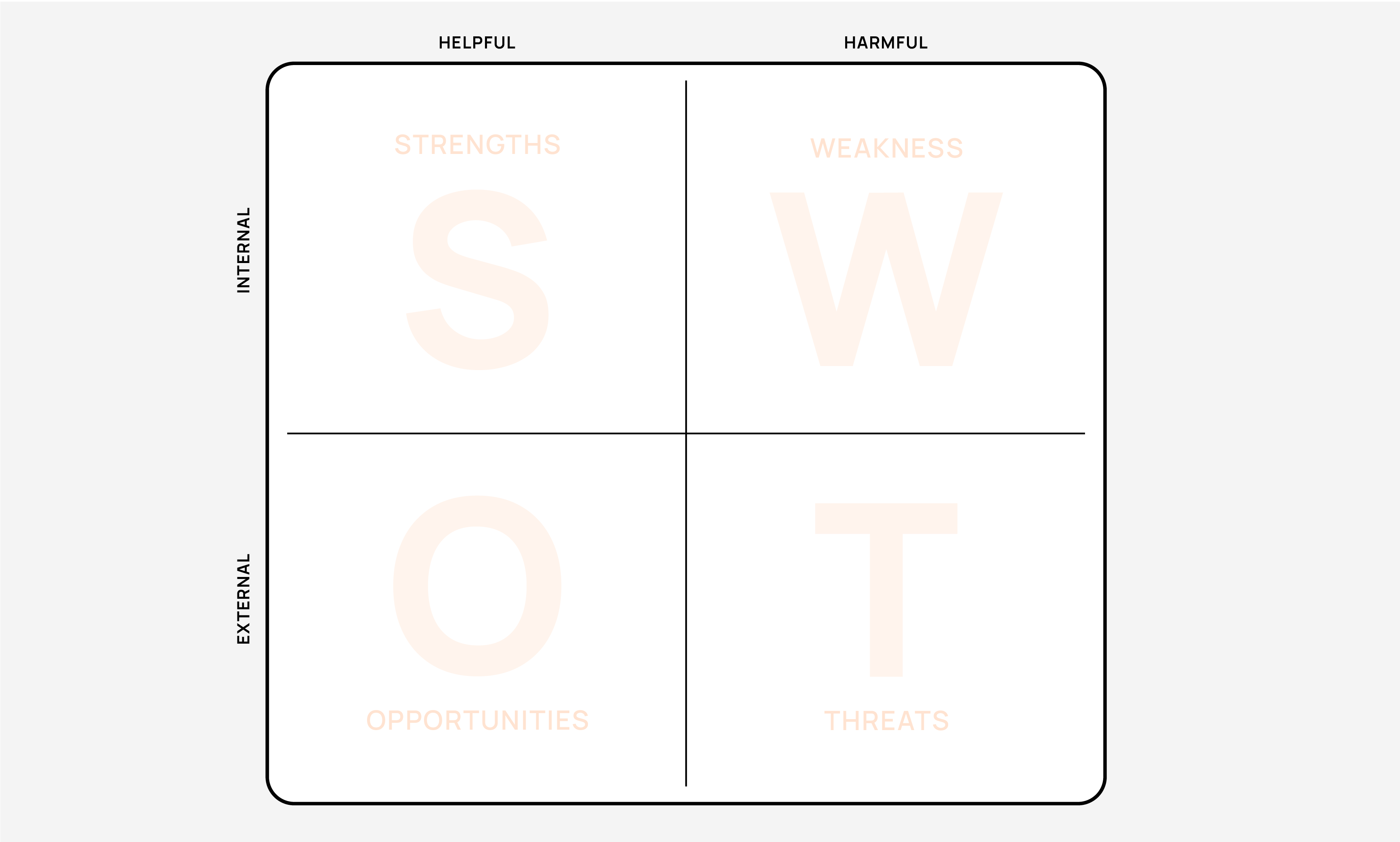
Strengths: Internal factors that provide advantages over competition
Weaknesses: Internal factors that hinder achieving organisational objectives
Opportunities: External chances for growth or improvement
Threats: External challenges the organisation might face
SWOT analysis helps organisations leverage strengths, address weaknesses, seize opportunities, and mitigate threats to achieve objectives.
The results
- A better understanding of the organisation’s competitive advantages
- Identification of potential threats and opportunities
When to use it
Strategic Planning: When evaluating or making strategic decisions
New Product Development: When creating new products or services
Strategic Projects: When undertaking projects that are most important to bring the organisational strategy to life
Strengths
Easy to use
Helps identify strategic options
Considers both internal and external factors
Weaknesses
Oversimplifies the complex
Dates quickly
Lacks prioritisation
How to use it?
What do I need to start?
Information relevant to the organisation or industry. For example:
- Internal insights: Sales figures, financial statements, and performance metrics
- External insights: Reports on market trends, industry analysis, and competitive landscape
- Stakeholder feedback: Input from customers, employees, suppliers, and partners
How to use it?
Who to involve?
SWOT can be done alone, or as part of a team. Consider including:
- Individuals who bring a strategic perspective and a big-picture view
- People who know the specific strengths and weaknesses of their teams
- People who can provide a fresh perspective to evaluate threats and weaknesses such as external advisors
Step by step
1
Define the objective
Define the objective of completing a SWOT.
2
Brainstorm internal factors
Examples of strengths or weaknesses include:
- Brand reputation and customer loyalty
- Financial resources
- Skills and capabilities
- Distribution networks
- Culture
Strengths
To understand the strengths of the organisation, ask questions like:
- What does the organisation do well?
- What resources does the organisation have?
- What is unique about the organisation?
- What advantage does the organisation have over competition?
Weaknesses
To understand the weaknesses of the organisation, ask questions like:
- What does the organisation lack?
- Where can the organisation improve?
- What might place the organisation at a disadvantage?
- What areas of the organisation are not performing as expected?
3
Brainstorm external factors
Examples of opportunities and threats include:
- Consumer demand changes
- Regulation changes
- Partnerships
- Economic changes
- Technological changes
Consider using PESTEL to more deeply explore external factors that could lead to opportunities or threats
Opportunities
To understand what opportunities exist for the organisation, ask questions like:
- What trends are emerging in the market?
- What technology developments might provide opportunities?
- What are customers seeking that isn’t being addressed?
Threats
To understand what threats exist for the organisation, ask questions like:
- Are there changes happening with competitors that could negatively impact the organisation?
- Are there changes to regulations that could negatively impact the organisation?
- Are there changes to economic conditions that could negatively impact the organisation?
4
Analyse
Consider the relationships between internal and external factors. Ask questions like:
- How do the strengths and weaknesses interact with the opportunities and threats?
- How can the organisation use strengths to take advantage of opportunities?
- How can the organisation improve weaknesses by exploiting opportunities?
- How can the organisation use strengths to counteract threats?
- How can the organisation develop plans to protect against threats and mitigate weaknesses?
Consider using TOWS Matrix to unpick these more fully.
5
Plan
Prioritise the chosen strategies.
This step is generally part of a broader planning process. Consider using the Balanced scorecard or Hoshin Kanri method to define objectives, initiatives and success metrics.