The means end chain
The Means-End Chain is a tool that maps how consumers connect product features to their personal values.
By uncovering the deeper reasons behind purchasing decisions, it helps businesses refine products and marketing to better meet customer needs.
The Means-End Chain has three main layers: attributes, consequences and values. Here’s an example using noise-cancelling headphones:
- Attributes (Means): The features of a product.
Headphones example: Active noise cancellation technology. - Consequences: The benefits gained from those features.
Headphones example: Reduces background noise for better focus. - Values (Ends): The deeper personal goals fulfilled.
Headphones example: Enhancing productivity and creating a more peaceful environment.
The results
- A clear map of how customer values link to the product’s features.
- A deeper understanding of why consumers purchase commodities.
- Better ideas for marketing messages.
When to use it
Customer Research: When uncovering what drives customer decisions and preferences
Product Development: When identifying which features will resonate most with consumers
Positioning & Messaging: When highlighting why your product matters to consumers on a personal level
Strengths
Customer focused
Connects features to values
Weaknesses
Time-consuming
Can be prone to interviewer bias
Complex for iterative product development
How to use it?
What do I need to start?
- A clear objective: Clarity on why completing a means end chain is important
- Target audience: Identify the group of consumers who will provide the most relevant feedback.
How to use it?
Who to involve?
The Means-End Chain analysis can be done alone or with a team. Consider involving:
- People who are responsible for product development or marketing
- People with the skills to conduct interviews
Step by step
1
Plan research approach
Define the scope of the research.
Determine which product features need to be explored and the type of insights required to connect these features to customer values.
Decide on the best research methods to gather these insights, considering time, budget, and the depth of understanding needed. Ask questions like:
- What features or attributes need to be understood better?
- What assumptions are being made about how consumers value these features?
- What research method (interviews, focus groups, surveys) will uncover the most meaningful insights?
- What resources are available for conducting this research?
Research methods to consider:
- Interviews: Useful for exploring how consumers emotionally connect with product features through open-ended questions.
- Focus groups: Great for group discussions to understand collective experiences and deeper motivations.
- Surveys: Ideal for gathering broader quantitative data on how features are valued, though less detailed on emotional insights.
- Literature review: Helpful to gather existing knowledge quickly, especially when budget or time is tight.
Questions you can ask customers:
- What features of this product stood out the most to you?
- How do these features benefit you in your daily life?
- What personal goals or values are most supported by these benefits?
- Why are these values important to you when choosing a product?
2
Undertake research
Complete insights gathering and summarise findings to extract key insights.
Consider involving a team in the synthesis process to validate ideas and gain different perspectives.
3
Map insights
Map out the insights collected, focusing on connecting product attributes to customer benefits and values.
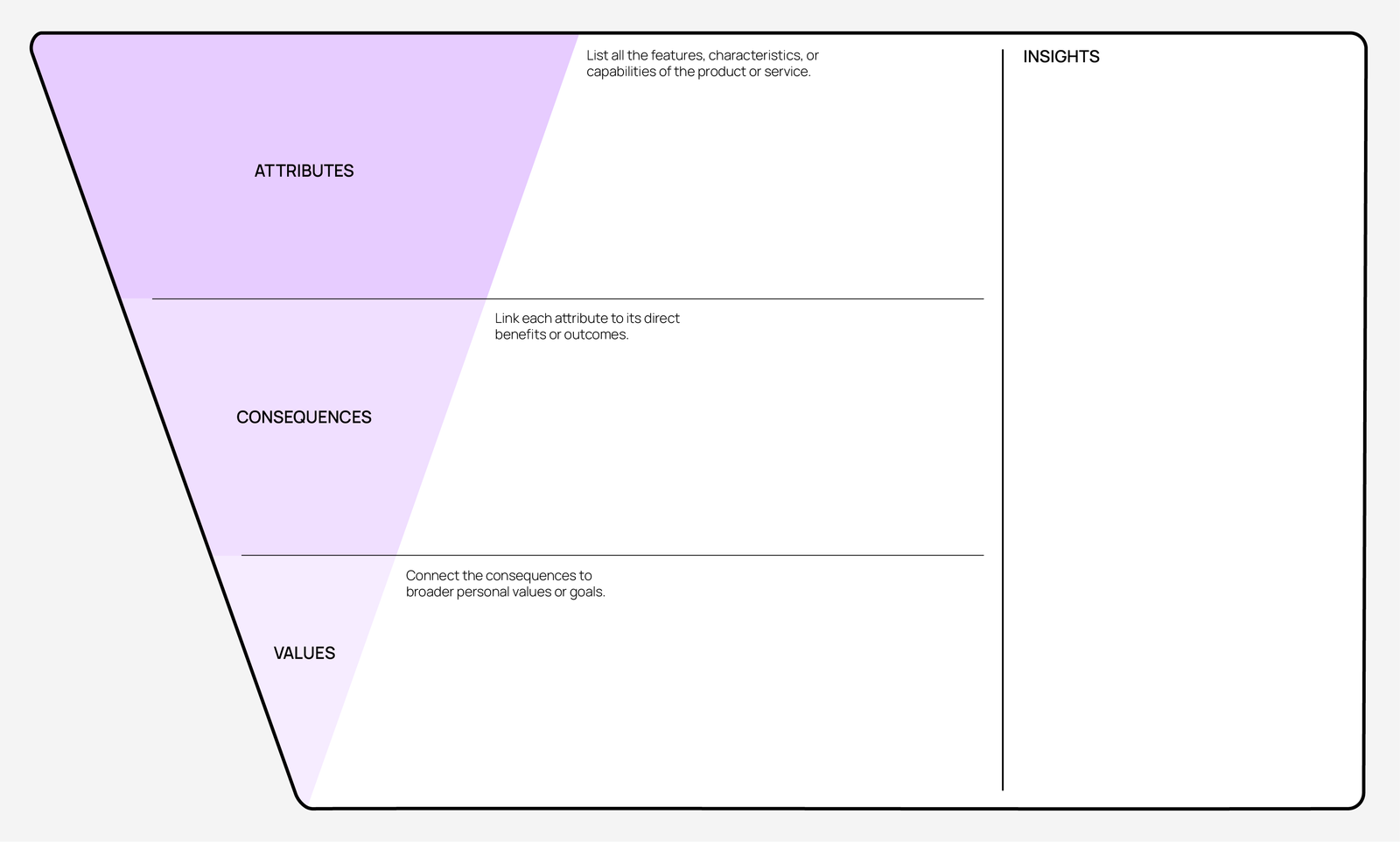
Identify product attributes (Means)
List all the features, characteristics, or capabilities of the product. Ask questions like:
- What are the key features of the product?
- What makes this product unique?
- How do these features compare to competitors’ products?
Determine consequences
Link each attribute to its direct customer benefits or outcomes.
Focus on how these attributes impact the user’s experience. Ask questions like:
- What are the direct benefits of each feature?
- How do these benefits improve the user experience?
- What problems do these benefits solve for the user?
Identify personal values (Ends):
Connect the consequences to broader personal values or goals. Ask questions like:
- What personal goals do these benefits help achieve?
- Why are these goals important to the user?
- How does the product align with the user’s core values?
4
Apply insights
Determine how the insights should be applied to both product development and marketing. Ask questions like:
- How can product development focus on the features that connect most to personal values?
- How can marketing messages highlight the link between product features and consumer values?
- What values should be central to the marketing strategy?
- How can we track the success of these insights in driving customer satisfaction and engagement?