Kano model
The Kano Model is a way to understand what customers want from a product or service. Kano sorts features into categories based on how they impact customer satisfaction.
Key concepts important in using the Kano Model:
1. Customer segments: Different customer groups that an organisation targets with products or services
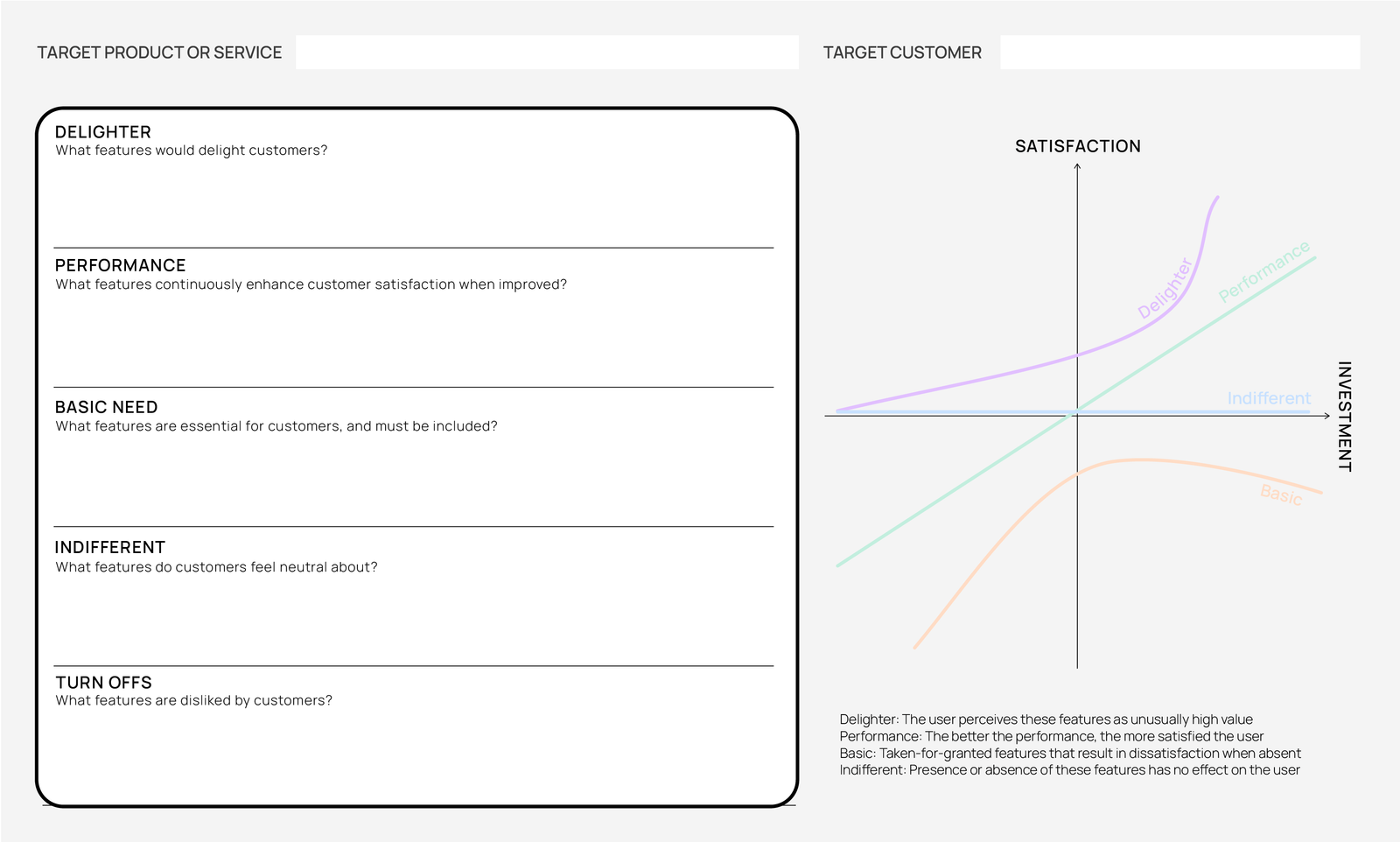
2. Kano categories. There are five categories. Basic needs, performance, delighter, indifferent and turn-off
Basic need: Things customers expect as a minimum requirement. If they’re missing, customers will not be happy
Example: making calls, sending texts, or accessing the internet
Performance: Things that can make customers happier as they get better
Example: battery life, charging time, storage
Delighter: Things that may not be expected, but that bring delight and satisfaction
Example: a pen for writing and drawing, innovative medical applications, ability to support virtual reality
Indifferent: Things that have minimal to no impact on satisfaction
Example: headphone ports, speaker volume
Turn-offs: Things customers don’t like
Example: Usage tracking which can be used for advertising purposes, a non-standard charger
The results
- A common view of customer needs
- Information to support decision making, such as prioritised features or improvements
When to use it
- Product Development: When creating or refining existing products
- Service Design: When designing or improving services
- Competitive analysis: When comparing a product or service offering with competitors
Strengths
Structured
Customer-centric
Supports prioritisation
Industry agnostic
Weaknesses
Can oversimplify customer needs
Can be subjective
How to use it?
What do I need to start?
- Clarity on target customer segments. Consider using customer segmentation analysis
- Target customer insights, such as survey on their needs, preferences, and behaviours
- Market research and competitive analysis
How to use it?
Who to involve?
- Representatives with product or service knowledge
- Representatives with skills and experience in marketing, design, and customer service
Step by step
1
Define the customer segments
Identify and agree on the most important customer segments. Each customer segment should have one canvas.
2
Compile customer and market insights
For each customer segment:
- Review existing customer insights to understand what customers need and expect.
- Consider any market trends which may influence customers needs in the future.
- Create a list of features including both existing and new features.
3
Group into Kano categories
Categorise each feature according to the Kano model: Basic, Performance, Delighter, Indifferent, and Turn-off. Questions to surface this include:
Basic Need: Which features are essential for customers, and must be included in the product or service?
Performance: What features, if improved, would enhance customer satisfaction?
Delighter: Are there any features that, if included, would pleasantly surprise and delight customers?
Indifferent: Which features do customers feel neutral about?
Turn-offs: Are any features disliked by customers?
4
Validate
Validate the categorisation with customers. This can be done using questionnaires or surveys . Consider using a Likert Scale to design surveys.
5
Prioritise features
Consider which features are most valuable. Aspects to consider are:
- Potential to satisfy customers
- Impact to the business
- Any investment required for implementation
Define a list of prioritised features. Consider using RICE or Weighted Shortest Job First to prioritise.
6
Implement
Determine how to implement the prioritised features. Consider drafting a plan or product roadmap that includes a staged timeline for implementation.