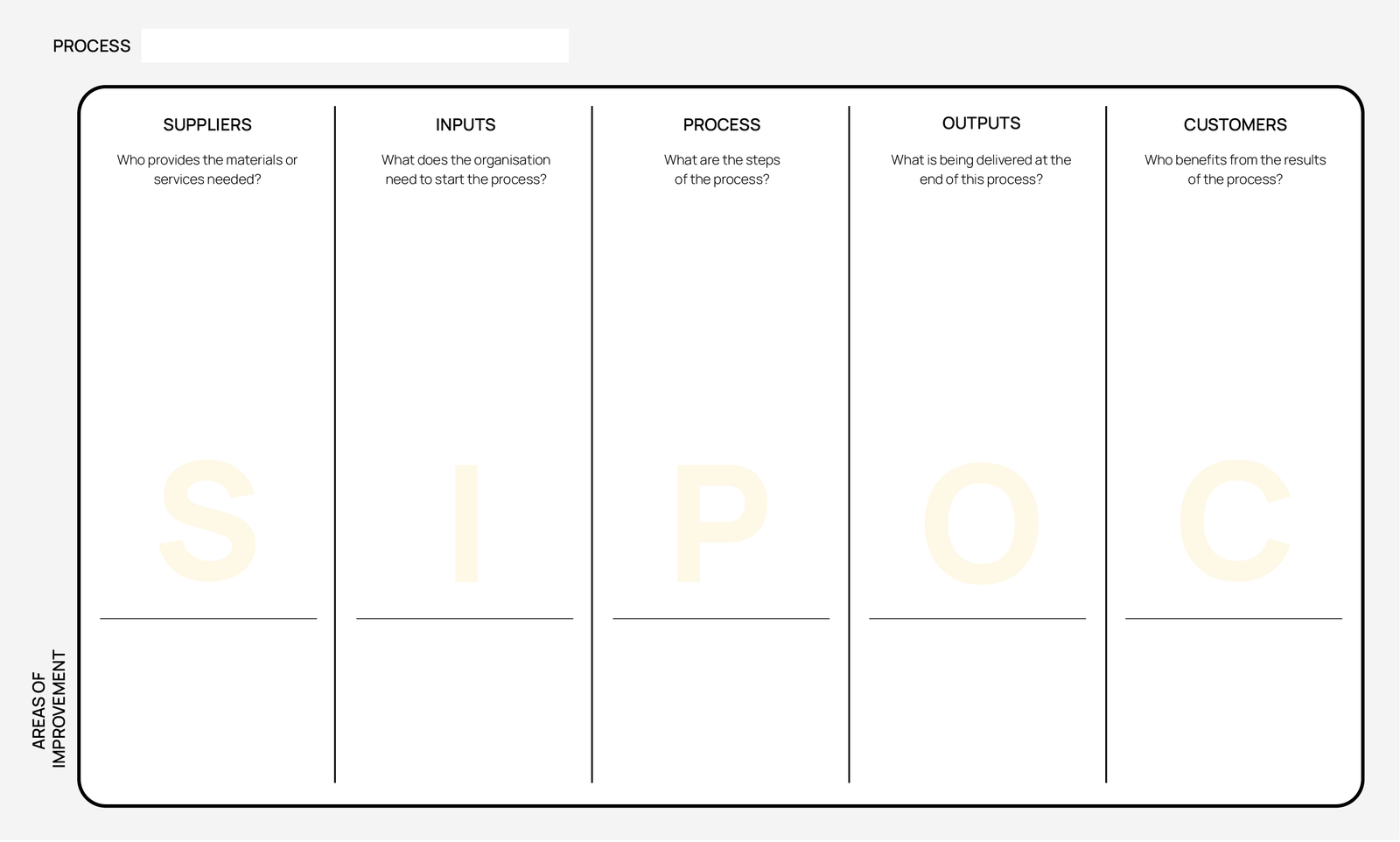
SIPOC Diagram
A SIPOC Diagram is a tool used to improve an organisation’s processes. SIPOC helps identify the key elements of a process: Suppliers, Inputs, Processes, Outputs, and Customers (SIPOC).
Here is an description of SIPOC and an example of SIPOC in practice using a bakery:
Suppliers provide the inputs needed for the process. These can either be internal or external sources.
Example: Flour supplier, water utility company, packaging supplier.
Inputs are the resources required to execute the process. This can include materials, information, or other essential items.
Example: Flour, yeast, water, salt, packaging materials, recipe.
Processes represent the actual steps or activities performed to transform inputs into outputs. You typically show this in a straightforward flowchart.
Example: Mix ingredients > Knead the dough > Let the dough rise > Bake the dough > Package the bread
Outputs are the results or products produced by the process. These could be goods, services, or information.
Example: Freshly baked bread, packaged and ready for sale.
Customers are the end-users or recipients of the outputs. They can be within or outside the organisation.
Example: Local grocery stores, individual customers, restaurants.
The results
- A visual outline of the process
- Identification of key elements in the process
- Identification of potential areas for improvement
When to use it
Process improvement: When identifying areas to enhance efficiency
New process design: When laying out a new process from scratch to ensure that all important elements are considered
Quality management: When seeking to meet compliance requirements and improve quality management systems
Strengths
Visual
Aligns team understanding
Standardises processes
Weaknesses
Inflexible for more complex processes
Time-consuming for larger processes
How to use it?
What do I need to start?
- An understanding of the organisation’s reason for existing
- Insights on the processes within the organisation
- A target process
How to use it?
Who to involve?
SIPOC can be done alone or as part of a team. Consider including:
- People who can offer insights into suppliers
- People who understand the process and outputs
- People who can offer insights about customers and competition
Step by step
1
Clarify the objectives
Determine the goal of mapping the process. Ask questions like:
- What problems are we aiming to solve by mapping the process?
- Who will use the SIPOC diagram, and what do they need from it?
- What are the critical aspects of the process to highlight?
- How will the SIPOC diagram help with decision-making or process management?
2
Define the high level process
Define the scope of the target process. Consider aspects such as the level of detail and the start and end points.
3
Populate each section
The segments of the SIPOC canvas can be populated in any order. Consider starting with the describing the process section.
Describe the Process
Break down the process into a series of steps.
Aim to keep the level of detail consistent throughout the process.
Identify Suppliers
List who provides the inputs for the process.
Determine Inputs
List the materials, information, and other resources required.
Identify Outputs
List the results or products delivered by the process.
Determine Customers
Identify who receives the outputs.
4
Validate and review
Review the SIPOC diagram.
Gather feedback from people involved in the process and refine as needed.
5
Analyse the process
Use the diagram to identify areas for improvement in the process. Ask questions like:
- Are there any issues with inputs from suppliers?
- Are there bottlenecks or delays in the process steps?
- Are all process steps necessary, or are there redundant activities?
- Are the outputs meeting the needs and expectations of customers?
- What are the root causes of any inefficiencies or problems identified?
6
Brainstorm solutions
Identify the areas that are most important to improve. Brainstorm improvements for the top problems. Ask questions like:
- What potential improvements can be implemented to address these issues?
- How would changes in one part of the SIPOC diagram impact other parts?
7
Prioritise improvements and plan actions
Prioritise improvements. Consider aspects like impact, feasibility, and urgency.
Create an action plan. Consider outlining responsibilities, and deadlines to implement the chosen improvements.