Double Diamond
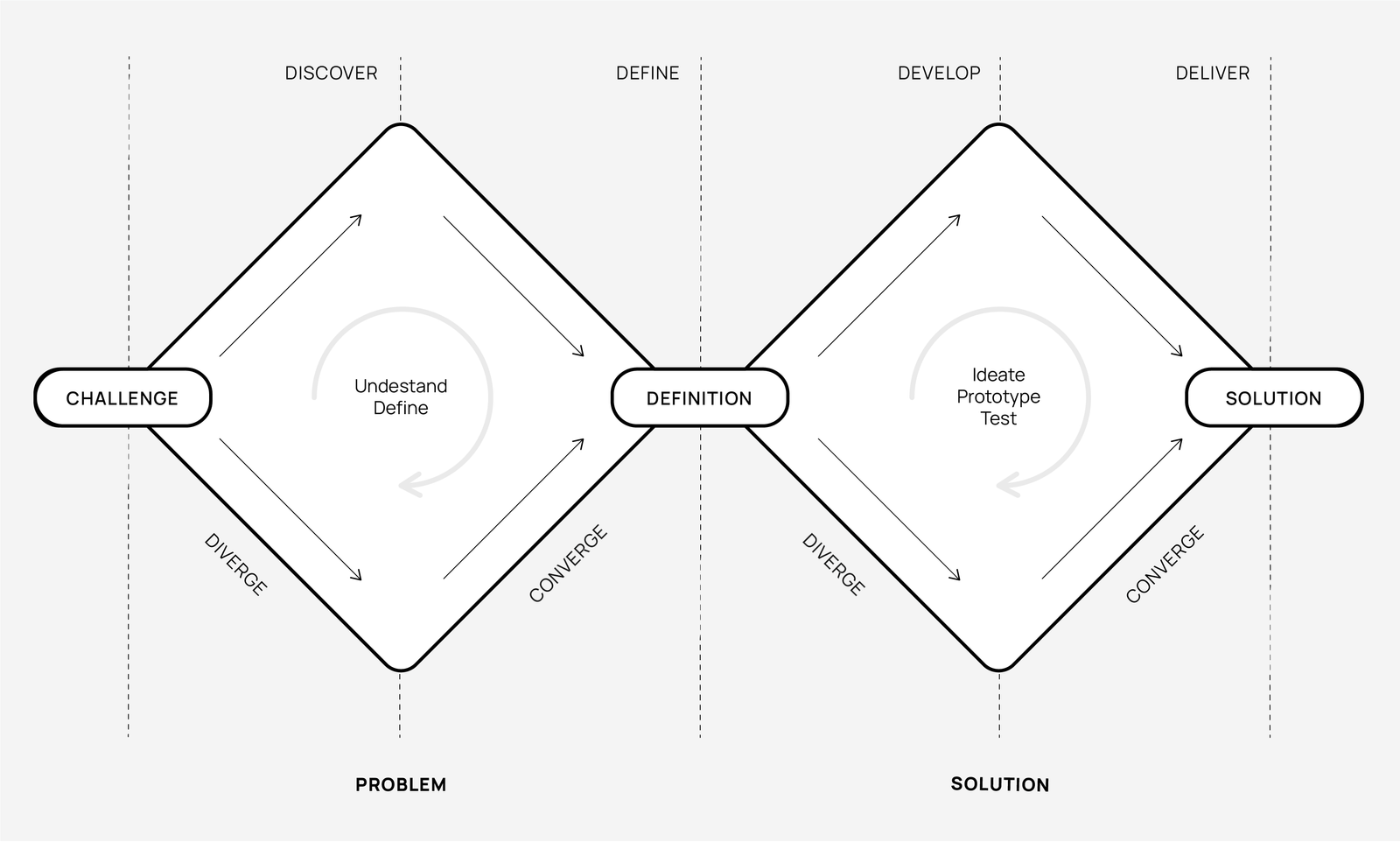
The Double Diamond is a structured approach to solving problems. It emphasises two key phases of thinking: divergent thinking (exploring a wide range of possibilities) and convergent thinking (narrowing down to the best option). Double diamond is divided into four steps:
- Discover: Gather insights and explore the problem space broadly to understand user needs and challenges
- Define: Narrow down the insights to clearly define the core problem to be addressed
- Develop: Generate and prototype ideas or solutions to solve the defined problem
- Deliver: Refine and implement the chosen solution, bringing it to life in the final product or service
The results
- A better understanding of what the end users need
- A practical solution to meet the end users needs
When to use it
Product and Service Development: When creating new products or services
User Experience (UX) Improvement: When seeking to improve the user experience of an offering
Problem Solving: When seeking to address complex issues that require deep understanding
Strengths
Structured approach
Emphasises exploration
Customer-centric
Promotes collaboration
Weaknesses
Emphasises exploration
Customer-centric
Promotes collaboration
How to use it?
What do I need to start?
What do I need to start?
- A challenge or opportunity statement
- Clarity on end users. For products and services customer segmentation analysis may be useful
- End user insights, such as their needs, preferences, and behaviours
How to use it?
Who to involve?
Double diamond is best done with a team. Consider including:
- People who will benefit from the solution
- People with strong design and problem solving skills
- People who are responsible for executing the designed solution
Step by step
1
Frame the challenge and opportunity
Refine the challenge or opportunity statement. Be prepared for this statement to change as insights are uncovered through the discovery phase.
2
Discover
Plan insights gathering
Determine the best approach to gather insights that support understanding of end users needs. Ask questions like:
- Who are the end users?
- What questions are we seeking to answer?
- How can we reach and engage end users effectively?
- What resources (budget, time, expertise) are available to conduct research?
- What quantitative methods (surveys, analytics) can provide insights?
- What qualitative methods (interviews, observations) can uncover deeper motivations and needs?
Consider using other design tools like customer empathy map and jobs to be done through discovery to compile and analyse insights.
Undertake insights gathering
Complete insights gathering and summarise findings to extract key insights.
Consider involving a team in the process to validate ideas and gain different perspectives.
3
Define
Refine the challenge statement based on insights gathered. Ask questions like:
- Is the core issue or challenge clearly articulated?
- Is the challenge statement specific enough to guide our design efforts?
- How will we know if we’ve successfully addressed this problem?
- How might this challenge evolve in the future, and how can we design a solution that is adaptable and future-proof?
Ensure that the challenge statement aligns with both end user needs and business objectives. Ask questions like:
- How does solving this problem align with our overall organisational goals?
- Are there any specific outcomes or objectives we aim to achieve through this solution?
Consider establishing goals or criteria that the design solution must meet. Ideally, these should be measurable and directly tied to addressing the identified problem or challenge. SMART goals can be helpful
4
Develop
Plan development approach
Define an approach to the ‘develop’ phase. Ask questions like:
- What methods will we use to brainstorm and generate a diverse range of ideas?
- Who will be involved in the idea-generation process?
- How will we capture and organise all generated ideas?
- How will we ensure that our idea-generation process encourages creativity and avoids premature narrowing down?
- What tools or techniques will facilitate effective idea generation? (for example, mind mapping)
- How will we involve end users in the idea-generation process?
- What is the timeline for generating ideas, and how will we ensure timely progress?
- What criteria will we use to evaluate and prioritise the generated ideas?
Undertake development
Generate solution ideas. Encourage creativity and exploration of different perspectives and approaches to solving the problem
Prioritise solutions
Identify solutions which have the most potential. Consider how well they solve the end users problem and meet the goals of the organisation.
Consider using prioritisation approaches like RICE, weighted short job first or impact/effort matrix.
Ask questions like:
- How directly does this solution address the core aspects of the challenge statement?
- How well does the solution align with the needs, behaviours, and preferences of the end users?
- Is the solution feasible given current capabilities and resources?
- How does this solution contribute to achieving specific organisational objectives?
Develop solutions
Develop conceptual designs or sketches based on the generated ideas. Consider creating storyboards or customer journey maps to visualise how end users will interact with the selected solutions.
Create prototypes or mockups of selected solutions. Prototypes can range from low-fidelity (paper sketches or wireframes) to high-fidelity (interactive digital prototypes)
Gather feedback on prototypes based on feedback and insights gathered during testing and iterate. This may involve refining prototypes, revisiting design concepts, or exploring new ideas that emerge.
Repeat the prototyping, testing, and iteration process until a refined and validated design solution is achieved.
5
Deliver
Plan delivery approach
Develop a delivery plan that considers the necessary resources to implement the solution effectively. Ask questions like:
- What steps are needed to finalise and implement the chosen solution?
- What tools or techniques will facilitate effective delivery? (for example, MVP or Kanban)
- What are the key milestones for this phase, and how will we track progress?
- How will we manage the rollout of the solution, including training and communication?
- What feedback mechanisms will be in place to monitor the solution’s performance?
Deliver
Execute the plan to deliver the solution, and monitor.